Post-trauma Neuropathic Pain
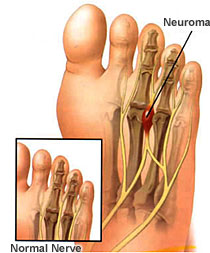
Interdigital neuroma is an example of post-traumatic neuropathic pain. Compression caused by running, wearing high narrow shoes and excessive standing results in the development of inflamed nerve tissue between the foot bones that is highly painful and has been described as being like walking on a hot pebble or having a hot poker thrust between the toes. Mortonís neuroma, the most common form, occurs between the third and fourth metatarsal bones of the foot.
In October 2006, the FDA granted orphan drug status for Adlea for the treatment of interdigital neuroma in patients who have failed conservative treatments, such as foot pads, NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and injections of corticosteroids, that would otherwise require removing or chemically destroying the nerve that causes the pain. Orphan drug designation is granted by the FDA to encourage companies to develop products that treat rare diseases and conditions and includes incentives such as market exclusivity for seven years, tax credits on qualified clinical trial expenses and a waiver of the FDA prescription drug user fees.
Approximately 216,000 patients in the United States suffer from interdigital neuroma, most often active females between the ages of 30 and 50. Currently available treatment options include orthotics, non steroidal pain relievers and steroid injections, which fail in approximately 50 percent of patients. Surgical removal of the neuroma requires a lengthy, painful rehabilitation. An alternative to surgical excision of the neuroma is infiltration with alcohol to lyse, or kill, the nerve. In both approaches, the result is permanent numbness in that portion of the foot. In some instances, the neuroma may regrow, causing a return of this painful condition. |
 |
